Last updated on... May 14th, 2020
Download Ready Boost Monitor for Windows to confirm whether your Ready Boost Device active or not. WinRAR (64-bit) IObit Uninstaller. Internet Download Manager. Avast Free Antivirus. Between 250MB and 32GB in size and up to eight devices for a total of 256GB (Windows 7 64-bit Enabling & Configuring ReadyBoost Insert a USB flash device into a USB 2.0 or higher port. The AutoPlay dialog box should be displayed automatically (unless you’ve changed the defaults in Control Panel).
Microsoft introduced this technology Ready Boost feature in Windows Vista, which promises to accelerate performance, which didn’t do well.
However, this feature actually works in Windows 7. You can use this Technology Ready boost in Windows 7 to speed up the boot process, data access, data processing, and system shutdown.

Let’s find out How to speed up Windows 7 with ReadyBoost
So What is “ReadyBoost”?
Windows ReadyBoost is a technology that uses free space on a flash drive commonly known as a thumb or USB drive to augment system memory.
ReadyBoost is a great way to make your computer faster and more efficient by increasing the amount of RAM, more like temporary memory, your computer can access.
This technology is basically designed to help when your PC’s memory is low. Readyboost works with most flash storage devices.
See also Which USB Flash Drive Is Best For Windows Readyboost
Windows 7, 8.1, 10 can handle more flash memory and even multiple devices, up to a staggering 256 GB of additional memory as ReadyBoost.
So How do you activate this Feature ? to speed up windows with ReadyBoost. If you have a fast USB flash drive available, give ReadyBoost a try with your Windows system and see the difference.
Steps to Speed up Windows With ReadyBoost
Plug your USB flash drive on to a USB port in your PC, if autoplay is enabled in your PC it will open your Flash drive, just close it.
Windows 7 Pro 64 Bit
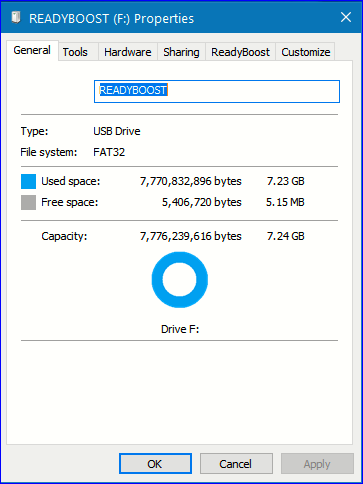
Click on your “My computer” in the My computer window locate your flash drive and right-click on the flash drive (as shown below).
3. From the menu that appears, scroll down and click on “Properties” you will see the following window as shown below
4. In this properties, window click on the tab “ReadyBoost” as shown above.
5. ReadyBoost window will give three options with radio buttons. Select the third radio button that says “Use this Device” and click to select.
Windows will warn you if there is not enough space (more on that later). Or whatever space is available on the flash drive can be used for your ReadyBoost.
Click on Apply then OK.
ReadyBoost starts immediately. You won’t need to use the Safely Remove Hardware feature to remove the flash drive, but if you remove the flash drive you lose the memory boost.
Now use your computer as usual. Windows Readyboost significantly speeds up the boot process, data access, data processing, and system shut-down.
Hello! I am Ben Jamir, Founder, and Author of this blog Tipsnfreeware. I blog about computer tips & tricks, share tested free Software’s, Networking, WordPress tips, SEO tips. If you like my post /Tips then please like and share it with your friends.
Related Posts:
Windows 7 supports Windows ReadyBoost, originally introduced with Windows Vista. Ready-Boost uses external USB flash drives as a hard disk cache, thus improving disk read performancein some circumstances. Supported external storage types include USB thumb drives asshown in Figure below, SD cards, and CF cards.
Unlike Windows Vista, Windows 7 recognizes that ReadyBoost will not provide a performancegain when the primary disk is an SSD. Windows 7 disables ReadyBoost when readingfrom an SSD drive.
External storage must meet the following requirements:
- Capacity of at least 256 MB, with at least 64 kilobytes (KB) of free space. The 4-GB limitof Windows Vista has been removed.
- At least a 2.5 MB/sec throughput for 4-KB random reads
- At least a 1.75 MB/sec throughput for 1-MB random writes
Unfortunately, most flash storage provides only raw throughput performance statisticsmeasured under ideal conditions, not the very specific 4-KB random reads required byReadyBoost. Therefore, the most effective way to determine whether a specific flash drivemeets ReadyBoost requirements is simply to test it. Windows Vista and Windows 7 automaticallytest removable storage when attached. If a storage device fails the test, Windows willautomatically retest the storage on a regular basis.
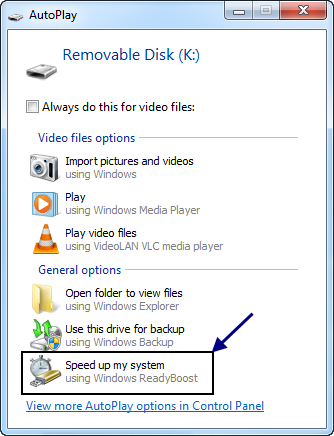
Some devices will show the phrase 'Enhanced for Windows ReadyBoost' on the packaging,which means that Microsoft has tested the device specifically for this feature. If you connect aflash drive that meets these requirements, AutoPlay will provide ReadyBoost as an option.
AutoPlay will prompt the user to use a compatible device with ReadyBoost.
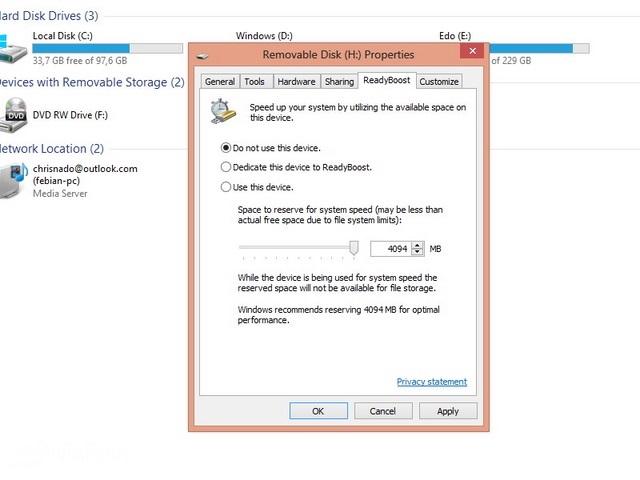
Alternatively, you can configure ReadyBoost by right-clicking the device in WindowsExplorer, clicking Properties, and then clicking the ReadyBoost tab. The only configurationoption is to configure the space reserved for the cache. You must reserve at least 256 MB.Larger caches can improve performance, but the ReadyBoost cache cannot be greater than4 GB on a FAT32 file system or greater than 32 GB on an NTFS file system.
Windows Vista and Windows 7 use the Windows SuperFetch algorithm (the successorto Windows Prefetcher) to determine which files should be stored in the cache. SuperFetchmonitors files that users access (including system files, application files, and documents) and preloadsthose files into the ReadyBoost cache. All files in the cache are encrypted using 128-bit AESif the flash storage device is removable, but hardware manufacturers can choose to disableencryption on internal, nonremovable ReadyBoost devices. Because the ReadyBoost cachestores a copy of the files, the flash drive can be removed at any point without affecting thecomputer-Windows will simply read the original files from the disk.
ReadyBoost provides the most significant performance improvement under the followingcircumstances:
- The computer has a slow hard disk drive. Computers with a primary hard disk WindowsExperience Index (WEI) subscore lower than 4.0 will see the most significantimprovements.
- The flash storage provides fast, random, nonsequential reads. Sequential read speed isless important.
- The flash storage is connected by a fast bus. Typically, USB memory card readers arenot sufficiently fast. However, connecting flash memory to an internal memory cardreader might provide sufficient performance.

Computers with fast hard disks (such as 7,200- or 10,000-RPM disks) might realize minimalperformance gains because of the already high disk I/O. ReadyBoost will read files from thecache only when doing so will improve performance. Hard disks outperform flash drivesduring sequential reads, but flash drives are faster during nonsequential reads (because ofthe latency caused when the drive head must move to a different disk sector). Therefore,ReadyBoost reads from the cache only for nonsequential reads.
Note In the author's informal experiments, enabling ReadyBoost on a 1-GB flash drive ona laptop computer with a WEI disk rating of 3.7 decreased Windows startup times by morethan 30 percent. Gains on computers with a WEI disk rating of more than 5 were minimal.
ReadyBoost creates a disk cache file named ReadyBoost.sfcache in the root of the flashdrive. The file is immediately created for the full size of the specified cache; however,Windows will gradually fill the space with cached content.
Windows 7 64 Bit Iso
To monitor ReadyBoost performance, use the System ToolsPerformanceMonitoring ToolsPerformance Monitor tool in the Computer Management console and add the ReadyBoostCache counters. These counters enable you to monitor how much of the cache is currentlybeing used and when the cache is read from or written to. It does not tell you exactly whatperformance benefit you are achieving by using ReadyBoost, however.